
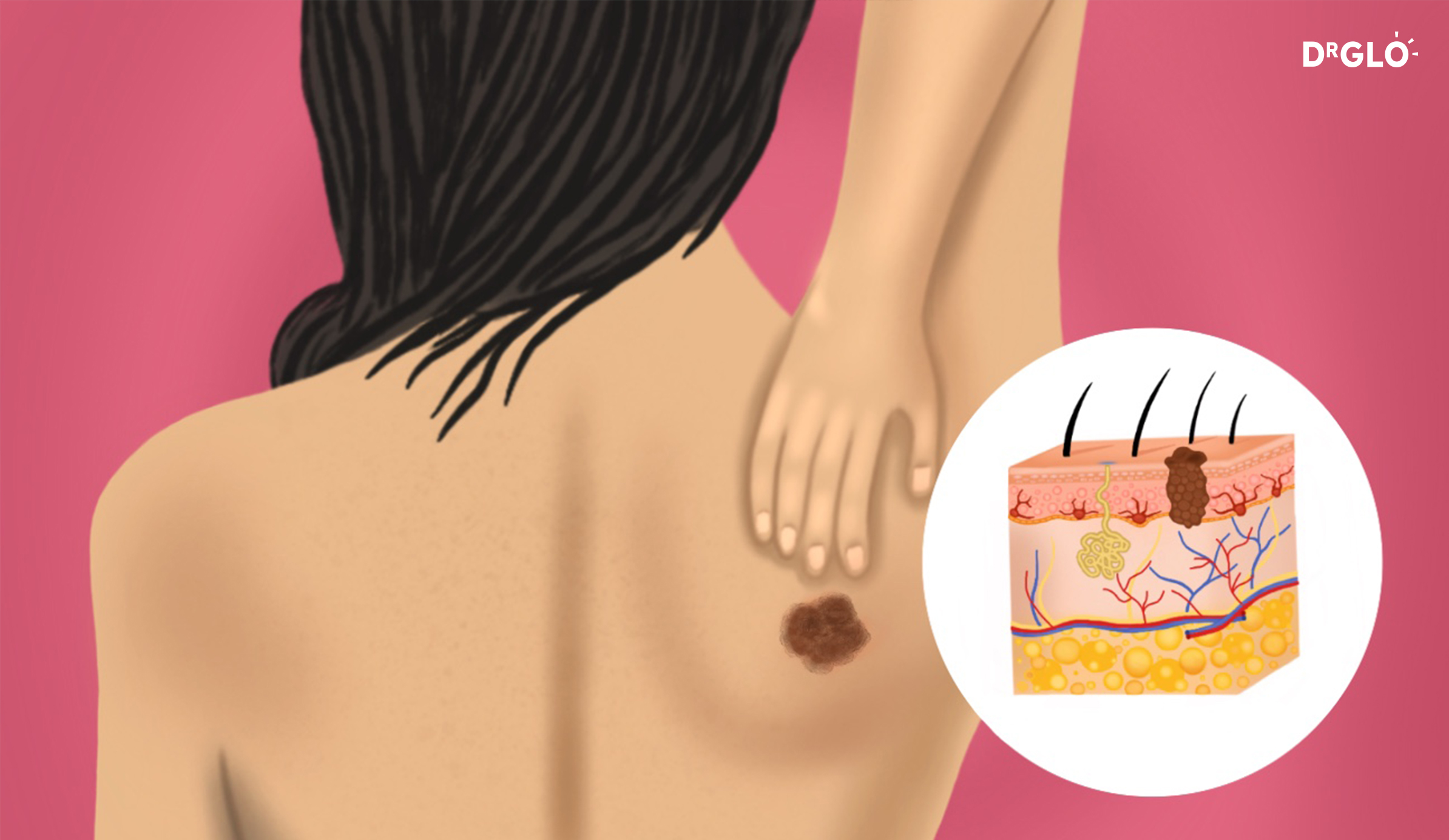
Skin Cancer Risk Assessment
High risk
- Family or personal history of melanoma
- Known gene mutations such as CDKN2A gene
- Unknown family history
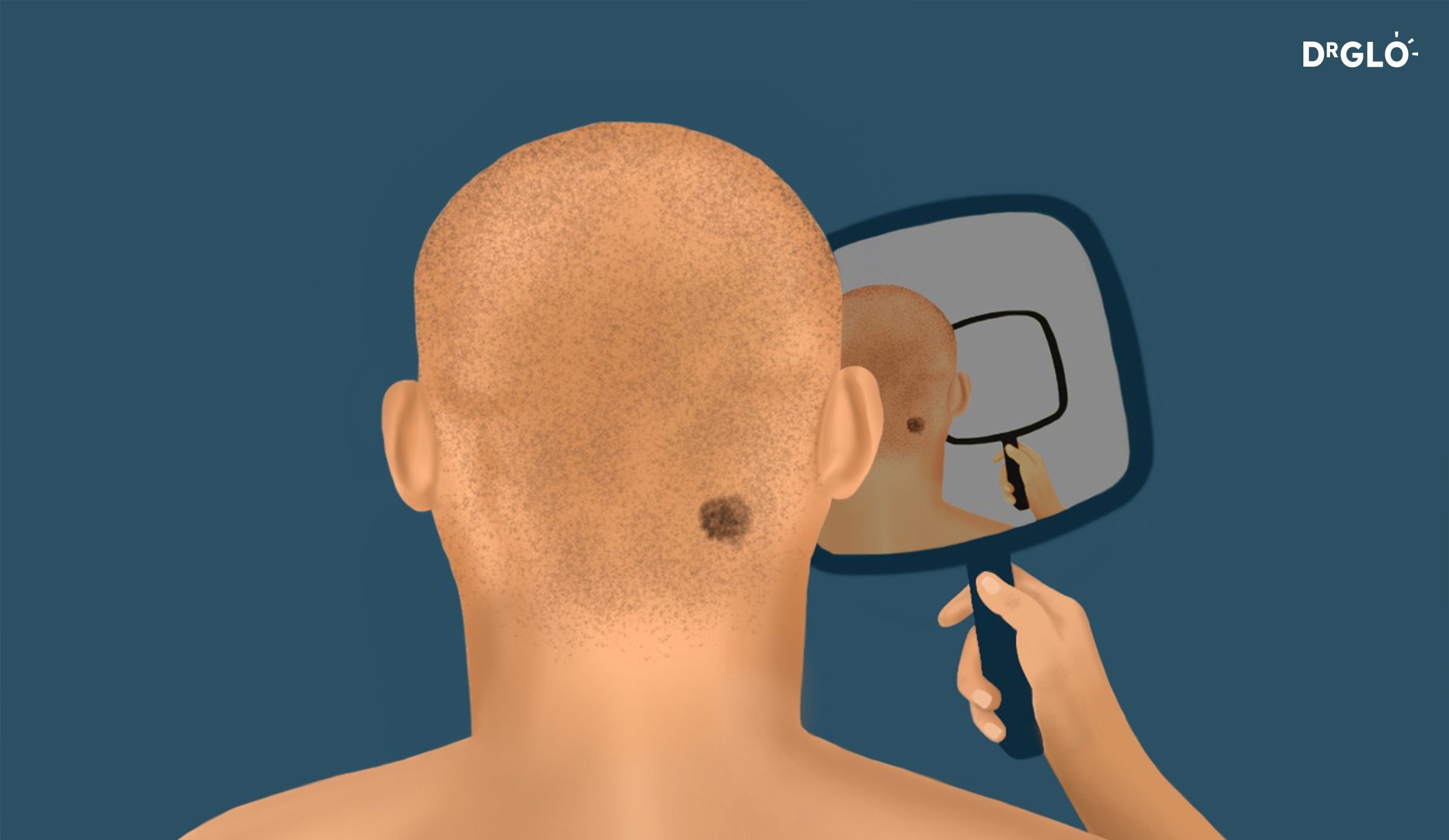
- More than 50 models on body
- Clinically diagnosed dysplastic nevus syndrome (where you have lots of unusual moles)
- Previous history of basal or squamous cell carcinoma (two types of non-melanoma skin cancers)
- Compromised immune system (due to medical conditions such as organ transplantation, underlying blood related cancers, HIV and AIDS, immunosuppressant medication use)
Moderate risk
- Outdoor work
- Significant outdoor recreational activities (sports/hobbies)
- Skin showing shows of sun damage
- Fair skin type with tendency to burn rather than tan
Low risk
- None of the above applies
SCAN QR CODE TO SHARE THIS ARTICLE
ADVERTISEMENT
 Common Skin Conditions
Common Skin Conditions Paediatric Conditions
Paediatric Conditions Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Infectious Skin Conditions
Infectious Skin Conditions Other Skin Conditions
Other Skin Conditions Treatment & Management
Treatment & Management Prevention & Skincare
Prevention & Skincare





Popular Articles